Everything You Need to Know About Form 16
Form 16 is a tax or a salary certificate for salaried employees issued by the Income Tax Department of the Government of India. This certificate contains comprehensive details about the employee’s salary, including the tax deductions done by the payer or employer, in the given financial year.
Table of Content:
What is Form 16?
Form 16 is essentially a tax certificate or document issued to Indian resident salaried employees by the Income Tax Department of the Government of India. The Form 16 document is issued under Section 203 of The Income Tax Act, 1961.
Form 16 is commonly called a “salary certificate”. This certificate contains comprehensive details about the employee’s salary, including the tax deductions done by the payer or employer, in the given financial year.
Income tax Form 16 components
For a salaried individual, income tax Form 16 is the most important income tax document. The Form 16 document is divided into two parts.
Part A
Part A provides a summary of the tax deducted by the employer or organisation from the employee’s salary income and deposited on behalf of the employee with the IT department. This certificate bears the signature of the organisation or employer and acts as proof that the employer or organisation has deducted income tax at source, i.e., from the salary of the employee, and deposited the amount with the IT department.
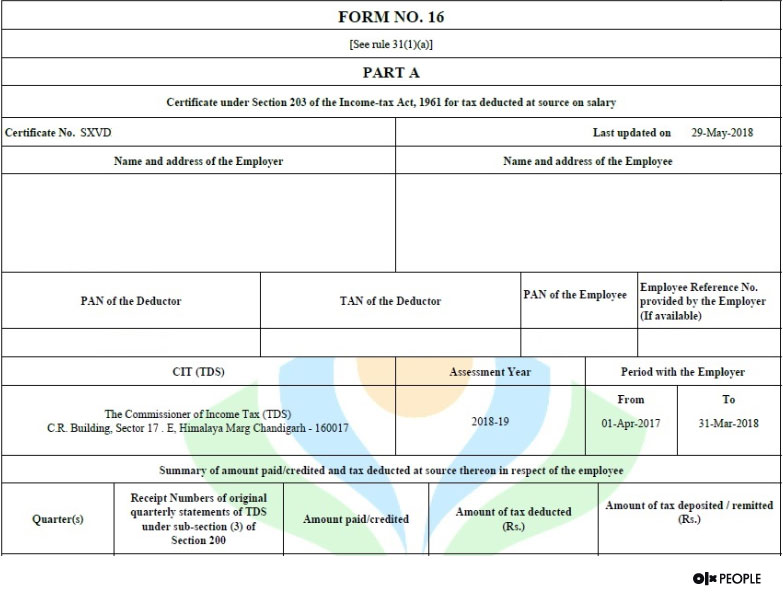
Details mentioned in Part A include:
- Personal information about the employer and the employee — This includes employer’s and employee’s names, addresses, PAN details, TAN details of the employer. TAN or TAX Account Number is the number given to the account that is utilised for the collection and deduction of taxes. These details enable the income tax authorities to analyse the money flow from the employer’s account to the employee’s account.
Note: The organisation is not eligible to collect TDS if it doesn’t have a TAN Number. In such cases, Form 16 will not be issued.
- AY or Assessment Year — This is defined as the specific year wherein the income of the taxpayer will get assessed. In simple terms, it is the particular year when the taxpayer applies for the income tax returns. For example — income or salary earned between 1st April 2019 and 31st March 2020, goes for assessment in 2020-21. So the Assessment Year is 2020-21.
- The employment period of the individual with the organisation during the given financial year
- The summary of paid salary
- Tax collection or deduction date from salary
- Details of quarterly tax deductions and tax deposits with the Income Tax Department
- Date of the tax deposition in the TAN account
- Acknowledgement number associated with the TDS amount payment
- The BSR Code of the bank from which payments were made, and the following Challan Numbers
Part B
This section is essentially a cumulative statement of the details of the total salary paid for the given year, other income sources as declared by the individual to the organisation, tax due and tax paid amount. The information is provided in an orderly and comprehensive manner in the prescribed format. Part B of the Form 16 mentions the employee’s total income earned along with deductions and exemptions as applicable thereof. All employee and employer name and contact details are also covered in this section.
Details mentioned in Part B include
- Total received salary: The structure of salary is divided into different components, which include Gratuity, Leave Encashment, Leave Travel Allowance, House Rent Allowance and others.
- Allowed Exemptions: According to Section 10 of The Income Tax Act, 1961, the allowances provided to the employees, such as HRA or House Rent Allowance, Conveyance Allowance, Hostel and School expenditure on children, medical allowance, etc. are mentioned in Part B of Form 16.
- Gross income: The total annual salary received by the employee and other income sources (for example, income from the property/house, etc.) is declared by the individual employee to the employer. The details of an additional source of income must be provided to the employer when the employees submit their proof of investments to claim deductions.
- Deduction from the salary: Deductions under Section 80C/80CCC/80CCD of the Income Tax Act includes the contributions done towards tax savings schemes or instruments, such as Sukanya Samriddhi, pension, life insurance policy, tax saving mutual funds, and Public Provident Funds. The maximum exemption limit is 1.5 lakhs INR.
- Net taxable salary: The total tax deductions are added under “Chapter IV-A”, and the amount gets reduced from gross annual income to determine the total taxable income. The tax liability of the individual is computed on this taxable amount.
- Surcharges and educational cess, if any
- Relief as per Section 89, if applicable
- Rebate as per section 87, if eligible
- Tax decision and tax refund or balance tax due
Details required from Form 16 while filing your return
The Form 16 format has been reconsidered for the current year by the Central Board of Direct Taxes (CBDT) which must be given to you by your employer. The structure of Form 16 to a great extent continues as before (containing Part-A and Part-B), the information given in it from this year is considerably more definite and broad when contrasted with that in the earlier years. Here is a list of things to cross-check with Form 16 before you file the return.
PAN : If the PAN number in your Form 16 is incorrect, the tax deducted from your monthly salary will not reflect in the Form 26AS. This is the first thing to crosscheck in your Form 16. If there is any correction, you need to consult your employer to edit the same.
Form 16 Part A: Part A of the Form 16 comprises the details of the tax deducted by your employer. It consists of the name, address, and PAN of the employee and TAN and PAN of the employer and summary of taxes deposited and deducted with the authorities against the employees’ PAN in each quarter. It has the details of the tax deducted from your salary, you need to cross verify these with your salary slips. The details of tax deducted shown in the Part A of Form 16 should match with the Form 26AS. If there’s any discrepancy between these two, the same must be reported to the employer immediately.
Form 16 Part B: This section shows the income related information of the employee. The income details given in the Part B of Form 16 will be extensive and detailed. If you are filing your returns via the Income Tax Department e-filing portal, all this information will be pre-filled. It’s important to cross check this information with the form.
Benefits of Form 16
Form 16 can be beneficial in a lot of ways. Here are some of the uses and advantages of Form 16.
File tax returns
Form 16 gives a detailed breakup of your salary components. The income details given in the form 1will help you to file tax returns. You can refer to it while filing returns.
Verify deposited TDS
Employers or the deductor can only issue a Form 16 after depositing the TDS to the government. So form 16 can be used as a proof that your employer or the deductor has deposited TDS to the government.
Calculating your liabilities
In the cases of miscalculations where the taxpayer has underpaid or overpaid the taxes, Form 16 helps to compute the accurate liability and it can be used to pay the remaining taxes for seek refund from the IT Department.
Loan and credit card applications
Financial Institutions consider Form 16 as a way to to determine the credit limit of the user. Most of the Institutions ask for the last 2 years of Form 16 while applying for a credit card. For loan applications, this form comes handy for assessing your application. Individuals should submit the tax filing details when applying for a personal loan, home loan, or vehicle loan. The lender will assess your financial health and repayment capacity based on your transactions mentioned in Form 16.
Form 16 types
Form 16 is of two types depending on the source of income of the individual:
Form 16A
When tax or TDS is deducted by the employer from the salary of the employee, the employer issues Form 16. Whereas, Form 16A is issued when tax is deducted from income apart from the salary.
For example — if TDS or tax is deducted from the earnings from the interest on fixed deposits, insurance commission, rent receipts, or other additional income that is subject to TDS deductions, then the individual will receive Form 16A.
This form details the total earnings through additional sources and the resultant tax deducted from this income and deposited against your PAN number. It also provides details about the name, contact details of the deductee/deductor, deductor TAN details, PAN details, and details of Challan of the TDS deposited by the deductor.
Form 16B
This TDS certificate is issued for deductions done on a property sale. Form 16B reflects the TDS amount subtracted from the total sale amount and is deposited by the buyer to the IT department. It is the duty of the buyer to deduct 1% as TDS on the total sale amount of the property during the sale. The buyer, then, has to deposit the amount collected as TDS to the Income Tax Department and furnish Form 16B to the seller as proof of the tax deposit.
Differences between Form 16, Form 16A and Form 16B
| Form | Form 16 | Form 16 A | Form 16 B |
| Purpose | Acts as the TDS certificate for the salary | Acts as the TDS certificate for income other than salary | Acts as the TDS certificate for sale of any property |
| Eligibility | Salaried individuals who fall under the tax brackets. | Taxpayers having TDS deductible income other than salary. Eg. Fixed deposits, Investments etc. | Taxpayer who has earned income from the sale of property (building or a part of it/land) other than agricultural land. |
| TDS Deducted by | The employer | Deductor (Bank, tenant etc) | Property buyer |
How to generate Form 16 or how to download Form 16 for salaried employees?
- Only the employer has the authority to generate, download and issue Form 16 to their employees. An individual is not authorised to download Form 16 online.
- Many employees are under the misconception that any employee can do income tax Form 16 download from the TRACES portal with the help of PAN, but this is untrue. Every salaried individual gets the Form 16 from their organisation or employer.
- Form 16 is also called the TDS certificate or salary certificate. If the company has deducted tax from the salary, then it is mandatory by law to furnish Form 16 to the employee, as Form 16 reflects that the tax is deposited with the IT department.
- The employer must issue Form 16 before the 15th of June of every year.
If you need any further information on how to get form 16 online, or if you want to know form 16 eligibility salary criteria or how to fill form 16 for salary with example, then connect with our expert consultants.
Form 16 – FAQs
- What to do when you have worked with one or more employers?
If you have changed jobs in the respective financial year, you need to ensure that the income provided by your previous employer is mentioned in the Form 16 provided by your existing employer. If it’s not mentioned, the taxpayer should submit the details from both the Forms while filing the tax returns and may have to pay additional tax accordingly. - Who is eligible for Form 16?
As per the Finance Ministry of Government of India, all salaried individuals who come under the tax brackets defined by the Income Tax Department are eligible for the Form 16. - Can we use Form 26AS instead of the Form 16?
The Form 26AS contains subtleties of tax deducted on behalf of the taxpayer by deductors (employer, bank, tenant etc.). TDS information that is given in Form 16/Form 16 A can be cross verified with Form 26AS. The TDS sums reflected in Form 26AS and Form 16/16A should always be the same. Both the forms, 26AS and 16 are equally important while filing your tax returns. - Is it mandatory for employers to provide Form 16?
The employer or deductor who deducts TDS (tax deducted at source) are legally bound to issue Form 16 to the employers or beneficiaries within the mentioned period by the authorities. - How is Form 16 different from Form 16A?
Form 16 A is a TDS certificate like Form 16. It is applicable for the cases where TDS is deducted from the income other than salary. For example, banks provide Form 16 A to the users, if they deduct TDS on the interest earned on fixed deposits. - Will the employer issue Form 16 if there are no taxes deducted from the salary?
Form is a TDS (Tax Deducted at Source) statement. If the income of the taxpayer does not fall under the tax bracket, the employer might not issue Form 16. Instead of Form 16, the employer will provide salary certificates on a monthly and quarterly basis. - Can I download Form 16 online?
Form 16 can only be downloaded and issued by the employer. No individual can download or access Form 16 by any other means. All salaried employees are eligible for receiving Form 16 from their employer.
Latest Updates on Form 16
The government issued relaxations for tax related deadlines, including Form 16, subject to the pandemic crisis. Considering the relaxation, employers can issue Form 16, on or before 15th of August 2020. The due date for ITR filing for FY 2019-20 has been extended to November 30, 2020. Employees who still haven’t got the Form 16 because of the employers who haven’t filed the TDS, have enough time till the end of November to file their returns.
Form 16 provides information about TDS/TCS for various transactions between deductor and deductee. As per the norms, Form 16 must be issued within July 15th every year. The Covid19 crisis has crumbled economies and financial plans around the world. The relaxations in the tax-related deadlines are indeed a relief for every taxpayer.
Subscribe For Newsletter
Subscribe to get the latest news and happenings around recruitment space


